The English and Dutch East India Companies: European Rivalry in Asia (1700-1800)
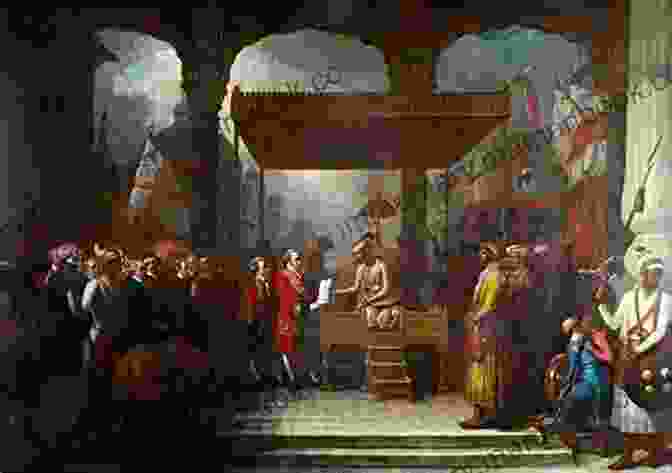


The Dutch and English East India Companies played a pivotal role in the development of European trade and colonialism in Asia during the 17th and 18th centuries. These companies established vast commercial empires that stretched from the Cape of Good Hope to the East Indies, bringing immense wealth and political influence to their home countries. This article delves into the history, rivalry, and legacies of these two powerful corporations.
Origins and Establishment
The Dutch East India Company (Vereenigde Oostindische Compagnie, or VOC) was founded in 1602 by a group of Dutch merchants seeking to establish a monopoly on the spice trade with the East Indies. It quickly became a powerful corporation, granted exclusive trading rights and military authority by the Dutch government.
5 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 4237 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Word Wise | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 243 pages |
The English East India Company (EIC) was founded in 1600 by a group of London merchants with similar aspirations. It initially focused on trade with India but later expanded into other parts of Asia. The EIC also enjoyed the support of the English government, which granted it a royal charter in 1600.
Territorial Expansion and Rivalry
As the East India Companies grew in power, they established trading posts and settlements throughout Asia. The VOC acquired control of the Dutch East Indies (now Indonesia),Ceylon (now Sri Lanka),and parts of India. The EIC established settlements in India, including Bombay, Calcutta, and Madras (now Chennai).
Rivalry between the two companies intensified as they competed for control of lucrative trade routes and territories. In 1623, the companies clashed in the Battle of Amboyna, resulting in a Dutch victory and the execution of several English traders. This event heightened tensions and led to further conflicts.
Economic Impact
The East India Companies had a profound economic impact on both Europe and Asia. They introduced new commodities to Europe, including spices, tea, and textiles, which became highly sought after and fueled a surge in demand. The companies also established plantations and commercial networks in Asia, which led to increased production and trade.
However, the companies' pursuit of profits often came at the expense of local populations. They exploited indigenous labor, sometimes using force or coercion. The companies' trading practices also disrupted traditional economic systems and led to social and political unrest.
Political and Administrative Roles
As the East India Companies expanded their territorial holdings, they assumed the role of political and administrative authorities. The VOCestablished a system of governance in the Dutch East Indies, including a governor-general and a council. The EIC also established a complex administrative structure in India, with a governor-general and provincial governors.
These companies played a significant role in maintaining law and order, collecting taxes, and administering justice. Their presence in Asia had a lasting impact on the political and social development of the region.
Decline and Loss of Power
The East India Companies faced numerous challenges in the late 18th century. Rising costs, mismanagement, and corruption weakened their financial position. They also faced increasing competition from other European powers, including the French and the Portuguese.
In the case of the Dutch East India Company, the Napoleonic Wars led to its bankruptcy and eventual dissolution in 1800. The British East India Company continued to operate in India but faced growing pressure from Indian nationalists and reformers. Following the Indian Rebellion of 1857, the company's rule in India came to an end, and control was transferred to the British Crown.
Legacies
The English and Dutch East India Companies left a complex and lasting legacy on Europe and Asia. Their pursuit of wealth and power had a profound impact on the global economy and led to the establishment of European colonialism in Asia.
The companies' commercial activities introduced new products and ideas to Europe, which influenced art, culture, and everyday life. Their territorial acquisitions also laid the foundation for future European empires in the region.
However, the companies' legacies are also marked by exploitation, oppression, and the disruption of local societies. Their practices had a lasting impact on the political, economic, and social development of Asia.
The English and Dutch East India Companies were powerful corporations that played a pivotal role in the history of European trade and colonialism in Asia. Their rivalry, territorial expansion, and economic impact shaped the course of global events. While their pursuit of profits brought wealth to Europe, it also led to exploitation and social disruption in Asia. The legacies of these companies continue to be debated and explored today, as we grapple with the complex and multifaceted nature of colonialism and its enduring effects.
5 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 4237 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Word Wise | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 243 pages |
Do you want to contribute by writing guest posts on this blog?
Please contact us and send us a resume of previous articles that you have written.
 Top Book
Top Book Novel
Novel Fiction
Fiction Nonfiction
Nonfiction Literature
Literature Paperback
Paperback Hardcover
Hardcover E-book
E-book Audiobook
Audiobook Bestseller
Bestseller Classic
Classic Mystery
Mystery Thriller
Thriller Romance
Romance Fantasy
Fantasy Science Fiction
Science Fiction Biography
Biography Memoir
Memoir Autobiography
Autobiography Poetry
Poetry Drama
Drama Historical Fiction
Historical Fiction Self-help
Self-help Young Adult
Young Adult Childrens Books
Childrens Books Graphic Novel
Graphic Novel Anthology
Anthology Series
Series Encyclopedia
Encyclopedia Reference
Reference Guidebook
Guidebook Textbook
Textbook Workbook
Workbook Journal
Journal Diary
Diary Manuscript
Manuscript Folio
Folio Pulp Fiction
Pulp Fiction Short Stories
Short Stories Fairy Tales
Fairy Tales Fables
Fables Mythology
Mythology Philosophy
Philosophy Religion
Religion Spirituality
Spirituality Essays
Essays Critique
Critique Commentary
Commentary Glossary
Glossary Bibliography
Bibliography Index
Index Table of Contents
Table of Contents Preface
Preface Introduction
Introduction Foreword
Foreword Afterword
Afterword Appendices
Appendices Annotations
Annotations Footnotes
Footnotes Epilogue
Epilogue Prologue
Prologue Lauren Scharhag
Lauren Scharhag John Garfield Barlow
John Garfield Barlow Richard Kostelanetz
Richard Kostelanetz John Cooper Clarke
John Cooper Clarke Emma Conway
Emma Conway Mary D Cornwell
Mary D Cornwell Robert Montgomery Bird
Robert Montgomery Bird Jim Dew
Jim Dew Chris Jarvis
Chris Jarvis Joe Haward
Joe Haward Adam Burningham
Adam Burningham Kevin Hogan
Kevin Hogan Elizabeth Davis
Elizabeth Davis Ada Ferrer
Ada Ferrer Mel Bay
Mel Bay Laurie Pfalzer
Laurie Pfalzer Darren Mitchell
Darren Mitchell Adam Alexander Haviaras
Adam Alexander Haviaras Craig Storti
Craig Storti John L Hosp
John L Hosp
Light bulbAdvertise smarter! Our strategic ad space ensures maximum exposure. Reserve your spot today!

 Fletcher MitchellEmbark on a Journey of Solitude and Adventure: A Comprehensive Exploration of...
Fletcher MitchellEmbark on a Journey of Solitude and Adventure: A Comprehensive Exploration of...
 Clarence BrooksBad Ops: The Agent Juliet Box Set - The Ultimate Collection for Spy Thriller...
Clarence BrooksBad Ops: The Agent Juliet Box Set - The Ultimate Collection for Spy Thriller... Steve CarterFollow ·8.7k
Steve CarterFollow ·8.7k Barry BryantFollow ·18.1k
Barry BryantFollow ·18.1k Stuart BlairFollow ·18.2k
Stuart BlairFollow ·18.2k Deion SimmonsFollow ·7.7k
Deion SimmonsFollow ·7.7k Hugo CoxFollow ·4.4k
Hugo CoxFollow ·4.4k Peter CarterFollow ·3.9k
Peter CarterFollow ·3.9k Arthur C. ClarkeFollow ·18.8k
Arthur C. ClarkeFollow ·18.8k Herman MelvilleFollow ·9.4k
Herman MelvilleFollow ·9.4k

 Kelly Blair
Kelly BlairSheppard Lee Written By Himself: A Journey of...
In the realm of...

 George Bernard Shaw
George Bernard ShawViper Naga Brides: Unveiling the Enthralling Fantasy...
In the realm of...

 Neil Gaiman
Neil GaimanOnce Upon a Hill in Tuscany: A Medieval Short Story
In the heart of medieval...

 Preston Simmons
Preston SimmonsBody Bereft: Exploring Loss, Love, and Legacy in Antjie...
A Poetic Requiem for the Lost:...

 Percy Bysshe Shelley
Percy Bysshe ShelleyThe Amazing Story Of Robert Smalls Escape From Slavery To...
The life of Robert Smalls is a testament to...
5 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 4237 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Word Wise | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 243 pages |